Weight loss, poor medicine, health, or conditioning, is the term for a lowering of the total body weight, because of mean decrease of fluid, unwanted weight or adipose tissue or lean mass, namely bone nutrients, muscle, tendon, along with other connective tissue. Weight loss may either occur unintentionally because of malnourishment or perhaps an underlying disease or arise from the conscious effort to enhance an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. "Unexplained" weight-loss that is not brought on by reduction in calorific intake or being active is called cachexia and might be a characteristic of a serious problem. Intentional fat loss is commonly termed as slimming.Intentional fat reduction is the decrease in total body weight as a result of efforts to further improve fitness and health, in order to change appearance through slimming. Weight loss in those that are overweight or obese helps to reduce health risks, increase fitness, and will delay the oncoming of diabetes. It could reduce pain and increase movement in those with osteoarthritis with the knee. Weight loss can cause a decrease in hypertension (blood pressure), however whether this reduces hypertension-related harm is unclear.Weight loss takes place when the body is expending more energy in work and metabolism as opposed to absorbing from food or another nutrients. It will then use stored reserves from fat or muscle, gradually leading to weight reduction. For athletes seeking to further improve performance or meet required weight classification for participation inside a sport, it isn't uncommon to search for additional weight-loss even if they can be already at their ideal weight. Others could be driven to shed pounds to achieve a shape they consider more appealing. However, being underweight is associated with health problems such as difficulty overcoming infection, osteoporosis, decreased muscle strength, trouble regulating temperature and even increased chance death.Low-calorie diets are also generally known as balanced percentage diets. Due to their minimal detrimental effects, these kind of diets are most frequently recommended by nutritionists. In addition to restricting calorie consumption, a well-balanced diet also regulates macronutrient consumption. From the overall number of allotted daily calories, it is recommended that 55% should result from carbohydrates, 15% from protein, and 30% from fats without more than 10% of total fat originating from saturated forms. For instance, a suggested 1,200 calorie diet would supply about 660 calories from carbohydrates, 180 from protein, and 360 from fat. Some studies advise that increased intake of protein may help ease hunger associated with reduced calorie consumption by enhancing the feeling of satiety. Calorie restriction in this manner has many long-term benefits. After reaching the desired body volume, the calories consumed per day could possibly be increased gradually, without exceeding 2,000 net (i.e. derived by subtracting calories burned by exercise from calories consumed). Combined with increased training, low-calorie diets are usually most effective long-term, unlike crash diets, which often can achieve short-term results, at best. Physical activity could greatly help the efficiency of an diet. The healthiest fat reduction regimen, therefore, is a that consists of a structured diet and moderate physical exercise.Weight gain has been regarding excessive intake of fats, (added) sugars, refined carbohydrates normally, and consumption of alcohol. Depression, stress or boredom could also contribute to weight increase, plus in these cases, folks are advised to search for medical help. A 2010 study discovered that dieters who got the full night's sleep lost a lot more than twice as much fat as sleep-deprived dieters.Though hypothesized that supplementation of vitamin D will help, studies don't support this. The majority of dieters regain weight in the lon run.According towards the Dietary Guidelines for Americans individuals who achieve and manage a healthy weight do this most successfully when you are careful to enjoy just enough calories to fulfill their needs, and being physically active. According towards the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), healthy individuals trying to maintain how much should consume 2,000 calories (8.4 MJ) daily.
Related Images with JAIC 2002, Volume 41, Number 3, Article 4 pp. 255 to 268
Galen eCalcs Calculator: Newborn Weight Loss Percentage Galen Healthcare Solutions
How to Calculate Weight Loss as a Percentage With Excel eHow
How to calculate body fat percentages
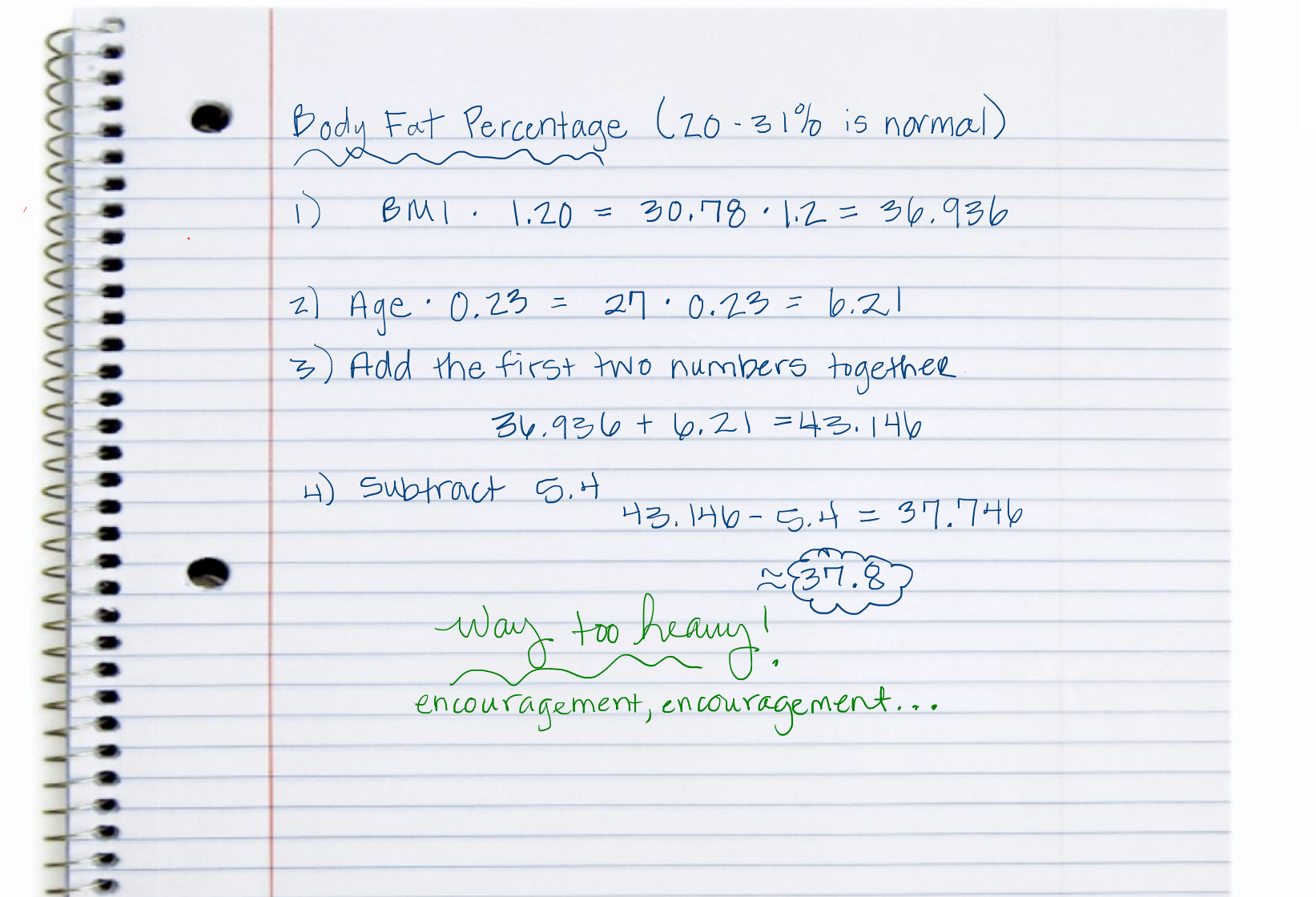
Komentar
Posting Komentar